Did you ever consider the dangers of Electric Forklift Accidents? Do you know how it effects your workplace? Here are the top 12 safety Electric Forklift Accidents protocols to be followed by everyone.
According to recent surveys, in the U.S. alone, forklift-related incidents cause almost 100 fatalities and over 34,000 serious injuries annually, with 70% of the electric forklift accidents being preventable by proper training and following safety protocols. Therefore, the prevention of electric forklift accidents is a semblance of work led by structured measures, which include operator training, checking the condition of the equipment, the use of safety devices, and safety culture.
Thanks to their environmentally friendly performance, silent operation, and low maintenance requirements, electric forklifts are becoming the main tool of the most modern warehouse operations. Nevertheless, these machines still entail serious safety risks if the users do not operate and maintain them well.
Today we represent the 12 foremost safety protocols every warehouse should introduce in 2025 to guarantee a safe, productive, and law-abiding working environment. Let us learn why they happen and precautions to be taken care of.
Top 12 Electric Forklift Accidents Safety Protocols for Your Warehouse
-
Pre-Operational Safety Inspections
Performing a detailed pre-operational inspection is an absolute prerequisite and the most instrumental measure in averting electric forklift accidents. These examinations allow a facility to discover the mechanical issues that are growing underneath the surface and turn them into safe situations.
Operators should always look visually and functionally at the forklift to be sure that the machine is safe to use before the beginning of the work shift. If one misses the opportunity to start with an inspection then they greatly increase the likelihood of brake failure, tire blowouts, or hydraulic leaks, e.g. situations which can lead to serious electric forklift accidents.
- Check the tire pressure, tread, and the overall condition of the surface to be sure the tires are not underinflated and have good stability and steering control.
- Look for any cracks, bends, and leaks in the forks, mast, and hydraulic hoses that may result in the reduction of the load-carrying capacity or sudden failure during work.
- Check all the controls such as steering, brakes, horn, lights, and emergency stop buttons to ensure that they are fully operational before starting the work.
To provide uniformity across shifts a standard digital or paper checklist should be used and documented. Facilities with telemetry systems can schedule these inspections as part of their fleet management software, thus allowing them to track in real-time and monitor compliance. Any discovered defects should be reported without delay, and the forklift should be taken out of operation until the issue is fixed.
-
Mandatory Operator Training and Certification
Electric forklift operation is a task a person can only take up after being trained and certified, a point supported by regulations. Comprehensive training schemes should cater to the theoretical knowledge as well as practical skills for the trainee to grasp safe operation standards, load handling, and emergency procedures. Certification is definitely not a single-term requirement—refresher training must be administered every three years or after an accident or unsafe behavior is observed.
- The training program must teach the operators about load capacity, center of gravity, and the dangers of overloading and unbalanced loads that result in tip-overs.
- Operators are required to get instruction on the specific models they will handle, such as controls, safety features, and emergency shutdown procedures.
- Included should be the practice of simulated drills scenes like battery fire, tip-over, and pedestrian collision in order to create operator latitude and readiness.
Employers have to keep the training logs as well as be in charge of the certification status of the workers. The investment in continuous education is the surest way of reducing human error which is the major source of forklift accidents.
-
Strict Enforcement of Speed Limits
One of the major reasons for forklift mishaps is the speeding of the vehicle particularly, resulting in tipping and hitting pedestrians or other stationary objects. Through the establishment and enforcement of explicit speed limits dependent on factors like aisle width, traffic density, and floor conditions warehouses are able to curb such kind of electric forklift accidents. Compliance with speed limits that enable the forklift to stop at the shortest possible distance is recommended by .
- To prevent unauthorized increase of speed, electric forklifts should be equipped with speed governors or programmable speed limiters.
- Using floor markings, signage, and audible alerts at intersections and high-traffic zones help familiarize operators with the need to reduce their speed.
- Through telematics systems that record speed infringements and create instant alerts for supervisors operator behavior can be observed and controlled.
Strict adherence to speed regulations together with enforcement of disciplinary measures for breach thereof creates a safety and accountability culture atmosphere which is awareness of such kind of matters and being responsible.
-
Proper Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Although the main attention is on the operator of the forklift, the rest of the warehousing staff are also obliged to wear the appropriate PPE so that in the event of an incident their injuries will be minimized. At all times, operators should put on their seat belts which, in the event of a rollover, are the most efficient ways of avoiding ejection.
Moreover, as both operators and workers must be provided with high-visibility vests, safety glasses, gloves, and steel-toed boots so that their safety is not compromised, the rest of the personnel need to wear safety helmets.
- Regular inspection of the seat belts is necessary to detect wear and tear and in case of damage, replacement should be done.
- Wear of high-visibility garments is of great help to both operators as well as pedestrians since through it they can easily be spotted especially in low-light areas or blind spots.
- Environment, where loading docks or racking zones are involved, is a place where people should wear hard hats as there could be the risk of overhead hazards.
It is not only necessary to have policies in place regarding the use of PPE but it is also important to ensure that the employees are aware of them and that their compliance is being monitored during the safety audits.
-
Safe Charging and Battery Handling Procedures
Electric forklifts are powered by either lithium-ion or lead-acid batteries, both of which require certain handling and charging procedures to avoid situations such as fire, chemical exposure, or electricity hazards. In contrast to lead-acid batteries, which must be charged outside or in a ventilated area, lithium-ion units can be recharged indoors; however, they should still be checked for overheating or cell imbalance.
- The location for charging stations should be clearly marked, and the area should be away from traffic and flammable materials.
- Operators should check the condition of the charging cables and connectors before every use and must never use wires that are frayed or have exposed parts.
- The installation monitored for errors, increased temperature, or charging issues that signal a malfunction is what the BMS or Battery Management System is.
Besides that, facilities have to educate their technicians about lockout/tagout procedures during battery servicing to avoid incident energization.
-
Load Handling and Stability Management
One of the main reasons for forklift tip-overs is the improper handling of the load. Understanding the concepts of load capacity, center of gravity, and mast tilt are some of the things that the operator should know in order to keep the forklift stable. The act of overloading or carrying unbalanced loads drastically raises the likelihood of electric forklift accidents.
- Make sure to always refer to the load capacity label and never go over the rated limit even if the load looks manageable.
- When driving keep the load low and tilted back as this will not only make the load more stable but will also give you better visibility.
- Do not raise or lower the load while the forklift is moving because the center of gravity will shift and the machine will most likely tip over.
There should be overload sensors along with load protection systems installed and tested continuously so that they can automatically give warnings or deactivate lifting functions when the limits are exceeded.
-
Pedestrian and Traffic Separation
Forklift-pedestrian collisions are one of the most frequent and most serious types of electric forklift accidents that occur in warehouses. points to the necessity of complete separation between pedestrian walkways and forklift traffic lanes as a solution. Employers should layout warehouses in such way that there is minimal interaction between moving machines and foot traffic.
- Physical barriers, floor markings, and warning signs should be utilized in order to separate pedestrian zones from forklift pathways and to make it clear to the pedestrians where these zones are.
- Mirrors or camera systems can be installed at blind corners and intersections to help with visibility.
- Spotters can be used or automated detection systems can be turned on when visibility is limited and at risk areas.
Besides regular safety meetings, safety briefing sessions should also emphasize the necessity of eye contact and communication between pedestrians and operators.
-
Routine Maintenance and Telematics Monitoring
Regular and preventive maintenance is the main factor to follow constantly for the safety and long service life of electric forklifts. By following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule one can easily find the causes of wear and tear before they result in failure. Telematics solutions facilitates this task by providing up-to-the-minute information about the condition of the equipment and the behavior of the operator constantly.
- Certified technicians should conduct regular inspections of the brake, steering, hydraulic, and electrical systems, as outlined in the manufacturer’s service schedule.
- Telematics can be used to keep an eye on the health of the battery, the efficiency of the motor, and the patterns of use that may signal the wrong or improper use of the machine.
- It is very important to keep detailed records of every maintenance work that has been done for compliance and auditing purposes.
- Immediate removal of a vehicle from the service which is in unsafe condition until it is fixed is a must.
-
Emergency Preparedness and Response
Even after considering all the preventive measures in place, emergencies are still possible. Aware of that fact, warehouses should prepare perfectly by outlining clear steps to follow in case of forklift-related incidents such as tip-overs, battery fires, or collisions.
- Emergency stop buttons should be installed where they can be easily reached by the operator and it should be ensured that they are in working condition.
- Competence of the first responders in the performance of their duties, such as evacuation, fire suppression, and first aid, should be provided through the training of the operators and supervisors.
- All employees should be drilled regularly, so they are aware of the procedures to follow when there is an emergency and the roles they have to play in a crisis.
In addition to that, there should be fire extinguishers specifically designed for electrical fires placed in a location that is easy to access near charging stations and areas that are at high risk which helps to reduce electric forklift accidents.
-
Use of Advanced Safety Technologies
Many modern safety features are present in today’s electric forklifts, which significantly decrease the likelihood of electric forklift accidents. Along with these integrated features, the employers should purchase the models that are equipped with the latest technologies such as collision avoidance, stability control, and automatic braking systems.
By the releasing of the accelerator, the automatic braking systems slow down the forklift and, thus, the risk of coasting in narrow aisles is greatly decreased.
For example, stability control systems employ various measures, such as adjusting power and brakes, to avert the rolling of the vehicle on the side of steep ground or on a surface where one part is flat and the other is uneven.
The main function of proximity sensors is to detect the presence of obstacles and pedestrian characters in a particular working area and to activate, for instance, providing alert sounds or light signals to the driver to warn of the approaching object/pedestrian. This combination of technology and human approach creates an additional safety buffer to avoid electric forklift accidents.
-
Clear Communication and Signage
Good communication is the key in a warehouse full of workers and machines. Operators have to clearly let know their movement to other workers so that no miss-communication can lead to electric forklift accidents.
- In order to alert the people nearby, horns and backup alarms should be used at crossings, blind spots, as well as when the vehicle is backing up.
- To help support the visibility efforts in areas with low-light conditions, installing flashing lights on forklifts is a good way to make the machine more apparent.
- By posting speed limit and no-entry zone signs, as well as the emergency procedures, throughout your warehouse you make sure your employees are aware of these regulations and can follow them easily.
- Hand signals that are standardized should be taught to all employees in order that they can use them in noisy places.
-
Safety Culture and Continuous Improvement
The establishment of a sound safety culture is one that is spearheaded by the top management and should be evident throughout the whole organization on a daily basis. Apart from setting an example, the supervisors by conducting frequent safety meetings and encouraging the employees to report near-misses, hazards, and other safety issues without fear of reprisal should reinforce this practice to secure from electric forklift accidents.
- Take advantage of monthly safety reviews to discuss safety related issues such as incidents, trends, as well as opportunities for improvements.
- Safe behavior can be motivated through acknowledgment and reward which, in turn, leads to compliance.
- Use of incident data gives you the chance to find underlying reasons and take steps to solve the problems by the implementation of corrective actions.
- Continuous development is what keeps safety measures up with changes in operations and new technologies.
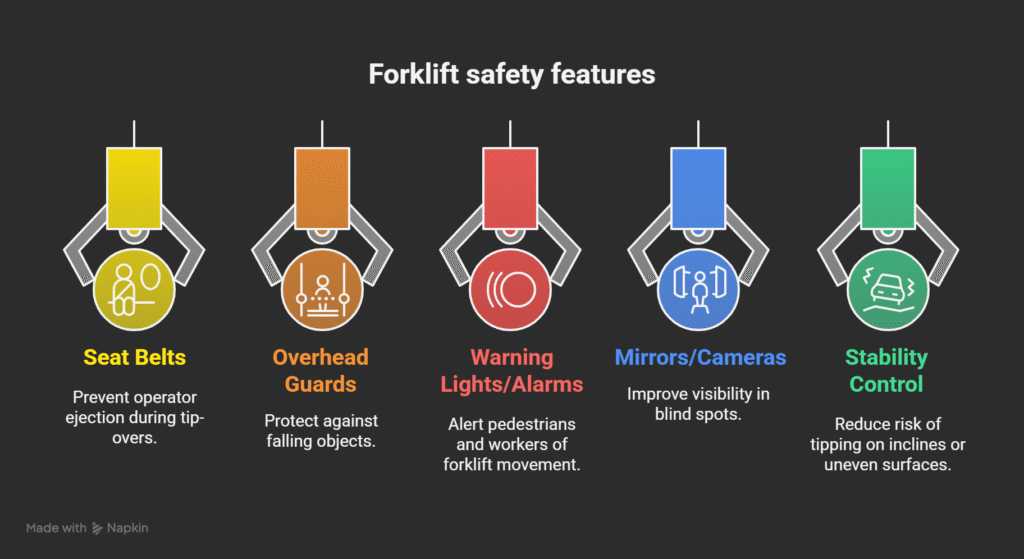
Safety Equipment and Functions
| Safety Equipment | Function |
| Seat Belts | Prevent operator ejection during tip-overs |
| Overhead Guards | Protect against falling objects |
| Warning Lights/Alarms | Alert pedestrians and workers of forklift movement |
| Mirrors/Cameras | Improve visibility in blind spots |
| Stability Control | Reduce risk of tipping on inclines or uneven surfaces |
Frequently Asked Questions – Electric Forklift Accidents
What is the most common cause of electric forklift accidents?
The most frequent causes that lead to such disastrous situations are highly speeding, improper load handling, untrained workers, and failure to conduct pre-operational inspections.
How often should forklift operators be retrained?
According to, refresher training is required every three years or immediately after an accident or unsafe operation.
Can electric forklifts be charged indoors?
Yes, lithium-ion electric forklifts can be charged indoors without the need for ventilation, unlike lead-acid models.
Why is wearing a seatbelt important on a forklift?
The main role of seatbelts is to keep the operator safe when the fork lift is overturned by preventing him from being thrown out to reduce electric forklift accidents. Being one of the leading causes of fatalities, this is how seatbelts save lives.
What should I do if my forklift shows a battery error?
You should immediately stop working with the forklift, locate a technician and inform him about the issue and according to the BMS(/) diagnostics, ask him to come for inspection.
How can I improve forklift visibility in my warehouse?
Some ways to improve forklift visibility in your warehouse are mirrors at corners, backup alarms, and flashing lights. Also, ensure proper lighting in the whole facility.
Are pedestrian zones necessary in a warehouse?
Exactly the separation of pedestrian traffic from that of forklifts is a key safety measure proposed by to drastically cut down on collisions between the two.